Chemistry on a skewer: if scientists well versed in cooking kebabs
Forming / / December 19, 2019
Preparation of a shish kebab, from the point of view of a chemist - a complex process, each stage of which there is a large number of delicate and interconnected reactions. If the matter is approached wisely recipe good kebab will associate with individual organic synthesis techniques - and even overtake them. And, as in the full scientific experiment, in the barbecue there are many details that affect the optimization of the process - and thus the taste and flavor of the final product.
So, to barbequing, you must perform two basic steps: marinate the meat and fry it on the coals. But first, let's understand that such meat - from the point of view of chemistry.
Meat
What we call the meat, and buy in the shop under the guise of beef and pork, is really a skeletal striated muscles of animals. Unless, of course, we will not be considered by-products, such as the heart, which are not used for barbecue. In addition to the actual muscle tissue, to include more meat fatty and connective tissue, which is adjacent to it.
Muscle tissue has a curious structure. We are accustomed to the fact that our body cells are usually very small, no discernible eye. Structural unit of muscle is the muscle fiber - and this is one large cage length of several centimeters and a diameter of hundreds of microns. It is formed at the junction of thousands of other cells, due to which a muscle fiber may be several thousand kernels.
The main property of the muscle fibers - the ability to shrink. That's how we (and other animals) to move the limbs - and not only. It provides special proteins - actin and myosin. This elongated molecules that form long bundles inside the cells. Under the action of external factors (nerve impulse), these tufts begin to move relative to each other, pulling the center. All fiber is divided into individual links - sarcomeres, stapled together.
In addition, meat contains high amounts of proteins elastin and collagen in the connective tissue. They are largely responsible for the mechanical characteristics of the meat (hardness, etc.). For the color of the meat meets the protein myoglobin. In general, the meat - this is largely a protein product, but, of course, and fat layers in it enough.
Pickling
The meat is marinated in order to solve several problems at once: to make it softer and give it extra flavor and hold the primary antimicrobial treatment.
Collagen molecules, which determines the hardness of the meat, which normally form strong fiber fibrils. This assembly occurs under the action of the hydrogen bonds - between attraction partially charged (polarized) amino acids moieties. Exactly the same communications occur between water molecules - between the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the other oxygen.
Many marinades possess acidic due to the presence of these acids - acetic often (e.g., fault, mayonnaise or vinegar), citric and lactic. Acidic environment and has a soy sauce, teriyaki sauce and - they contain a large amount of pyroglutamic acid and succinic, citric, formic and acetic.
This means that in marinades have a lot of hydrogen cations, which are capable of binding to protein molecules, protonating them. This alters the charge distribution in molecules and gives a fine structure of the hydrogen bonds, which leads to a change in the geometry of the protein molecules. As a result, denaturation of proteins: collagen and actin fibers swell, soften, collagen gradually dissolves.
The same effect can be achieved without the use of acids. For example, some tropical fruits such as pineapple and papaya contain enzymes which degrade collagen and elastin to single amino acids, and a protease bacteria and fungi are able to degrade proteins similarly muscle fibers. There are physical techniques to mitigate meat - holding at a pressure of several thousand atmospheres, which also leads to denaturation of proteins.
The speed with which the pickling of meat, also depends on the composition of the marinade. For example, it has been proven that the presence of alcohol in the marinade marinating process accelerates. This is due to the fact that the lipid membrane of cells is more soluble in alcohol than in water. Also a role in mitigating the meat play a variety of auxiliary substances - such as the tannins in wine and beer.
It is worth noting that marinating does not always lead to a softening of the meat. In some situations, when an excessive pickling (in the presence of too much acid or alcohol) fabrics lose water and become too solid. The same effect can be achieved if overcook the meat - then most of the water out of it simply "fly away."
The second most important effect - anti-microbial. But the responsibility for it is not only acid, but other marinade ingredients, such as onions. Different ways to destroy harmful organisms in meat devoted quite a lot of research in one of the most curious authors have proposed to add to the standard procedure of marinating meat in beer and more treatment in an ultrasonic bath.
It should be noted that the second phase barbecue starts synthesis of some carcinogens - harmful substances with the potential to cause cancer. This applies in particular to products charring fat dripping onto the coals. Among them is benzo [a] pyrene and other polyaromatic hydrocarbons.
Another class of carcinogens that occurs when charring meat, - heterocyclic amines. These compounds are able to form complexes with DNA and affect the vital functions of cells. One study even foundDietary Benzo [a] Pyrene Intake and Risk of Colorectal Adenoma correlation between frequent consumption of smoked or grilled meat with some types of cancer. Accordingly, it is recommended to reduce the possibility of the use of such substances. But here can help marinating.
There are several studies conducted by the Portuguese and Spanish chemists, which indicate that certain types of marinade reduce the likelihood of formation of these carcinogens. For example, pickling in dark beer partly inhibitsEffect of Beer Marinades on Formation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Charcoal-Grilled Pork formation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and to reduce the share of the resulting heterocyclic amines should be selected based marinades wine, beer or even containing tea. In general, the impact of marinades to education in general, polyaromatic hydrocarbons are still not well understood. Among other possible inhibitors include onion, garlic, spices and marinades with citric acid.
fry-up
Pickling, due to the denaturation of most of the proteins greatly speeds up the process of cooking meat. This avoids the prolonged exposure to heat and evaporate too much water. Along with the acceleration of protein denaturation, roasting on coals in meat triggers many other chemical processes.
The first of them - a well-known Maillard reaction. It is responsible for the formation of strong-smelling organic substances that give a special smell of roasting meat. In this reaction come amino acid found in meat, and sugar. As a result of complex formation heterocyclic compounds, derivatives of furan, thiophene, alkylpyridinium and pyrazines.
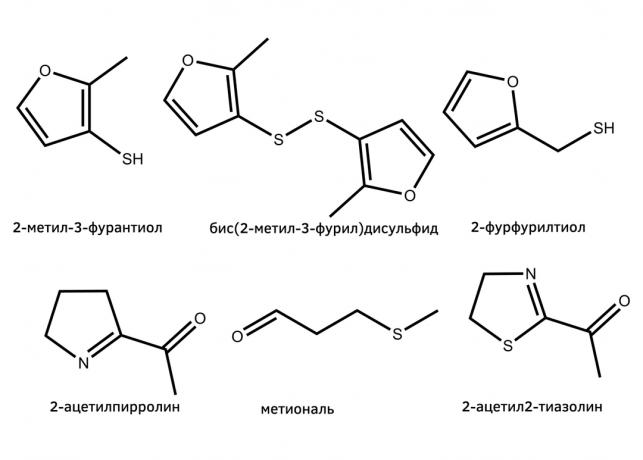
A specific flavor profile of each type of meat his own, he is defined by the concentration of thousands of aromatic substances, formed when frying. In the case of fried chicken and pork important role in the flavor play condensation products of cysteine with sugars, e.g., 2-methyl-3-furantiol and its dimer, and 2-furilmetantiol.
With sugar, of course, react, and other amino acids. Methionine, for example, interacting with the sugars is subjected to degradation methional - the substance has a smell of chips.
It is understood that the proteins and sugars are not only in meat. Therefore, the Maillard reaction plays a role in the flavor of other foods. For example, the odor of baking (and some varieties of rice) due atsetilpirollinom-2, the product of the reaction between proline and sugars. Small amounts of this substance occurs in roasted meats.
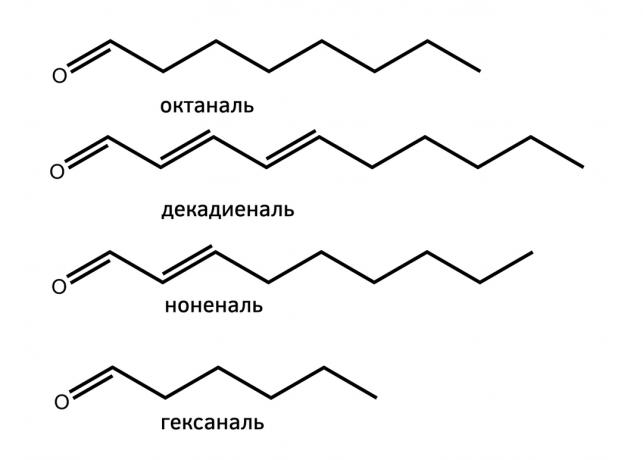
The second chemical process - carbonization fats. Fats - are esters of glycerol and fatty organic acids, such as stearic, palmitic, and so on. If the heat treatment they are chemically converted to aldehydes, such as geksadekanal, hexanal, and so on. Interestingly, the roast beef contains more aldehydes than chicken and pork, and that makes them different tastes. A characteristic smell arises due lamb 4-octanoic and 4-methylnonanoic acids.
The third process - a reaction between the products of fats and charring products of the Maillard reaction. It sorts alkanethiols, alkylpyridinium, alkyl derivatives of thiophenes, pyrroles, thiopyranes, thiazoles and so on. The alkyl part of them comes from the fat components, and heterocyclic - from mayyarovskoy.
In addition, when roasting meat are other reactions with amino participation. Thus, cysteine and glutathione form during heat treatment and tritiolany dithiazine, which also contribute substantially to the odor.
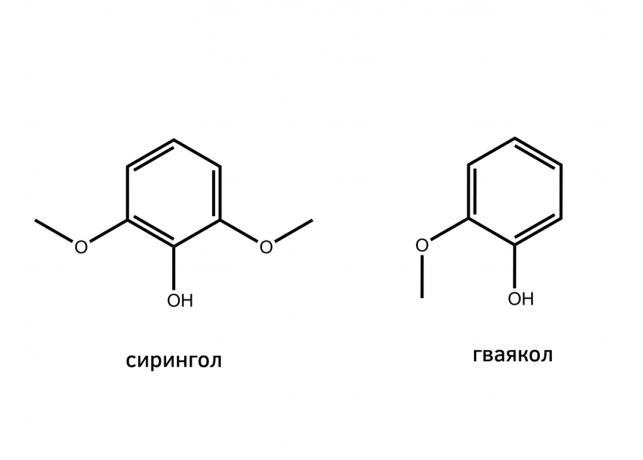
The taste and aroma of shish kebabs give not only the products of decomposition of amino acids, sugars and fats, but also the products of coal combustion. Among them stands out siringol (its name, incidentally, comes from the Latin name of lilac, Syringa vulgaris) and guaiacol - they are formed during the decay of the lignin binder for the cellulose molecules in the wood. These substances give kebab (or barbeque) characteristic smell of smoke.
The ratio of aromatic substances in the cook barbecue affect tens technical details cooking temperature, duration of the roasting coal choice meat marinade marinating time. And it's a great opportunity to, armed with the scientific method, to find their best recipe barbecue and maybe even write about this scientific article - with a particularly juicy description of experimental part.
see also
- How to fry a delicious barbecue. Chef reveals the secrets →
- TEST: How much do you love to barbecue? →
- 5 incredibly simple way to do BBQ with your hands →

