First aid - a complex of urgent measures aimed at saving human lives. Accident, sudden onset of disease, poison - in these and other emergency situations require competent first aid.
According to the law, first aid is not health - it is up to the arrival of medical or delivery of the victim to the hospital. First aid can be any person who is in a critical moment next to the victim. For certain categories of citizens first aid - official duties. We are talking about the police, traffic police and emergency, military, firefighters.
The ability to provide first aid - simple, but very important skill. IN emergency it could save someone's life. We present our 10 basic skills in first aid.
The algorithm first aid
In order not to get confused and competently provide first aid, it is important to observe the following steps:
- Make sure that the first aid you are not in danger, and you do not put yourself at risk.
- Ensure the safety of the victim and others (for example, remove the victim from the burning car).
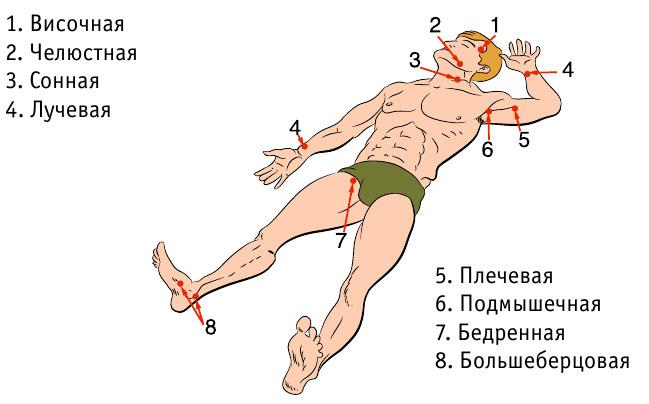
- Check availability at the victim for signs of life (pulse, respiration, pupillary reaction to light) and consciousness. For breath testing is necessary to tilt the head of the victim, to bend to his mouth and nose and try to hear or feel the breath. For the detection of the pulse must be applied to the fingertips of the carotid artery affected. To assess consciousness is necessary (if possible) to take the victim by the shoulders, gently shake and ask any question.
- Call the experts: 112 - mobile phoneWith city - 03 (emergency), or 01 (rescue).
- To provide emergency first aid. Depending on the situation, it can be:
- airway;
- cardiopulmonary resuscitation;
- stop bleeding and other events.
- Provide affected the physical and psychological comfort, await the arrival of experts.
Artificial respiration
The artificial lung ventilation (AV) - is the introduction of air (or oxygen) in the human respiratory tract in order to restore the natural ventilation of the lungs. It refers to basic resuscitation.
Typical situations requiring mechanical ventilation:
- car accident;
- incident on the water;
- shock and others.
There are various methods of mechanical ventilation. The most effective first-aid layman considered artificial respiration mouth to mouth and mouth to nose.
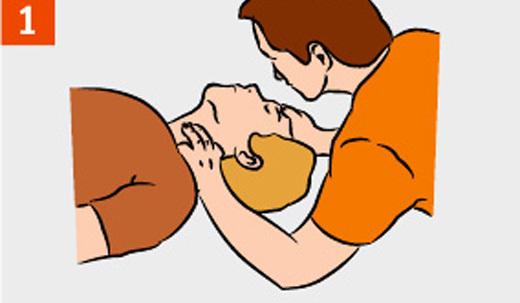
If the inspection of the affected natural breathing is detected, conduct artificial respiration should be immediately.
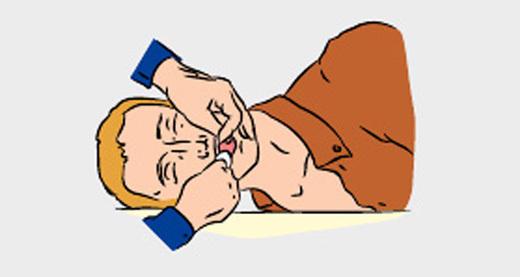
Equipment of artificial respiration mouth to mouth
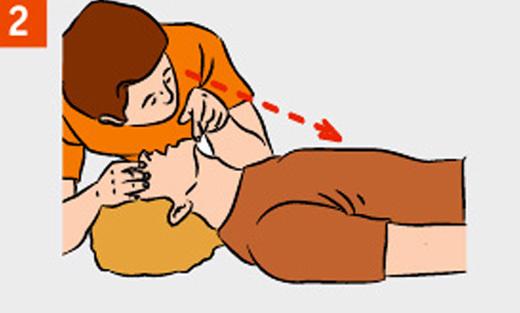
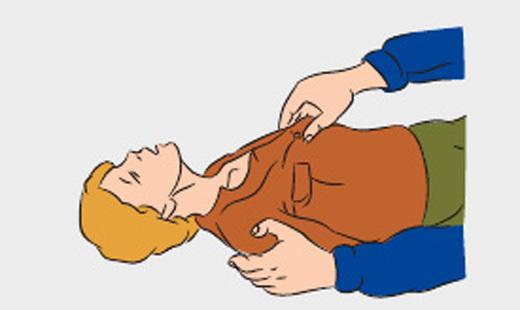
- Provide patency of the upper airway. Turn victim's head to the side and remove the finger from the mouth mucus, blood, foreign objects. Check out the nasal passages of the victim, clean them if necessary.
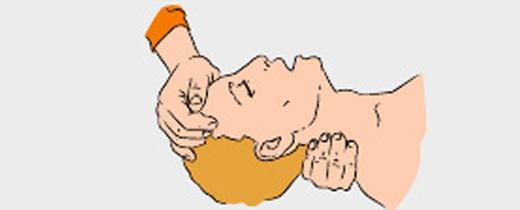
- Zaprokinte victim's head, holding her neck with one hand.
Do not change the position of the head of the victim with a spinal injury!
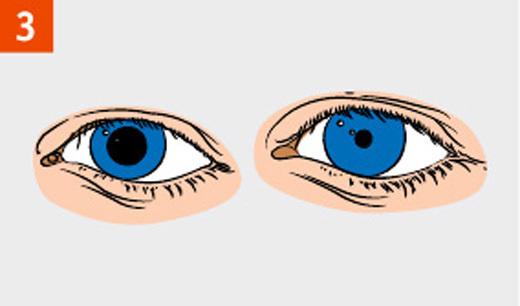
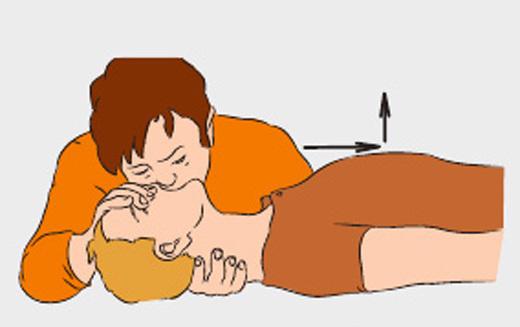
- Put on the victim's mouth napkin, handkerchief, a piece of cloth or gauze to protect themselves from infection. Pinch the nose of the affected thumb and forefinger. Take a deep breath, firmly press the lips to the mouth of the victim. Breathe into the lungs of the victim.
First 5-10 breaths should be fast (20-30 seconds), and then - 12-15 breaths per minute.
- Keep track of the movement of the chest of the victim cell. If the chest of the victim at a breath of air rises, it means you're doing well.
Chest compressions
If there is no breathing, along with heart rate, you need to do chest compressions.
Indirect (closed) cardiac massage or chest compressions, - a contraction of the muscles of the heart between the sternum and the spine in order to maintain the human blood circulation in cardiac arrest. It refers to basic resuscitation.
Attention! It is impossible to carry out chest compressions in the presence of a pulse.
Technique chest compressions
- Place the patient on a flat hard surface. On a bed or other soft surface to carry out chest compressions can not.
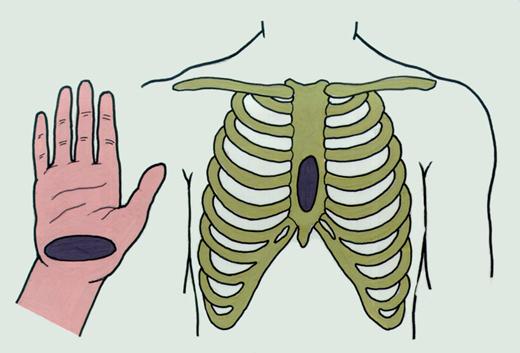
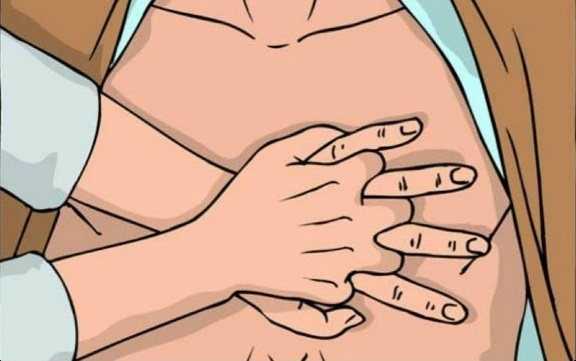
- Determine the location of the victim xiphoid. Xiphoid process - it is the shortest and narrowest part of the sternum, its ending.
- Measure 2-4 cm up from the xiphoid process - this compression point.
- Place the base of the palm to the compression point. In this case, the thumb should point to either chin or on the stomach of the victim, depending on the location of the person performing resuscitation. On top of one hand put a second hand, fingers fold into the lock. Pressing conducted strictly base of the palm - your fingers do not touch the chest of the victim.
- Perform rhythmic tremors chest much smoothly vertically, the weight of the upper half of your body. Frequency - 100-110 compressions per minute. In this case, the chest should bend at 3-4 cm.
Infants chest compressions performed the index and middle finger of one hand. Teenagers - the palm of one hand.
If simultaneously with the chest compressions performed ventilation, every two breaths should alternate with 30 chest compressions.


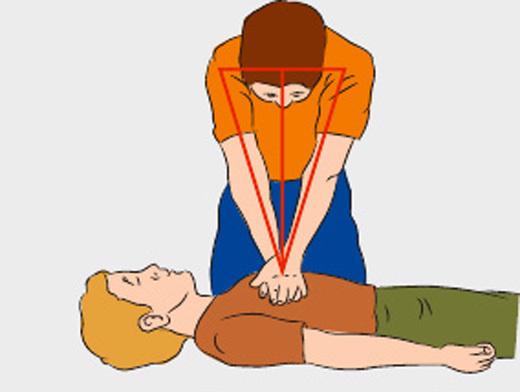

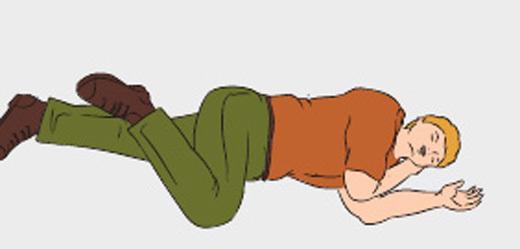
If during resuscitation at the victim regain his breath and there was a pulse, stop first aid and lay the person on his side, putting his hand under his head. Keep an eye on its condition before the arrival of doctors.
Admission Geymliha
After contact with food or foreign bodies in the trachea, it is sealed (fully or partially) - a man suffocates.
Signs of airway blockage:
- Lack of proper breathing. If the windpipe clogged is not fully man coughs; if completely - it held by the throat.
- Inability to speak.
- Bluish skin, swelling of the neck vessels.
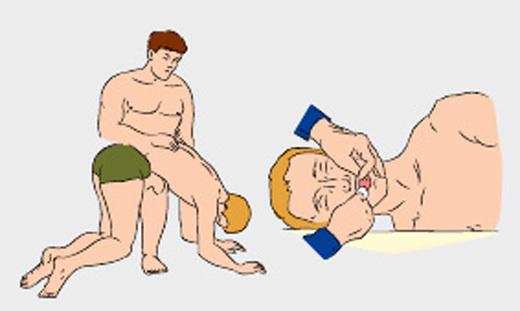
Cleaning of the respiratory tract is most often carried out by the method Geymliha.
- Stand behind the victim.
- Clasp his hands, clasping them in the lock, just above the navel, below the costal arch.
- Press firmly on the abdomen of the victim, sharply bending the elbows.
Do not squeeze the chest of the victim, except for pregnant women who are pressing carried out in the lower part of the chest.
- Repeat the technique a few times, until the airway is not freed.
If the victim has lost consciousness and fell, lay him on his back, sit on his hips with both hands push the costal arch.
To remove foreign matter from the respiratory tract of the child to rotate on its belly and pat 2-3 between the blades. Be very careful. Even if the baby is quickly cleared his throat, see your doctor for a medical examination.



Bleeding
Stop the bleeding - it measures to stop the loss of blood. When providing first aid we are talking about stopping external bleeding. Depending on the type of vessel is isolated capillary, venous, and arterial bleeding.
capillary hemostasis is accomplished by blending aseptic dressings, as well as if injured arm or leg, raising the limb above the level of the body.
When venous bleeding compressive bandage is applied. For this is done tamponade wounds: the wound is applied gauze is placed over it several layers of wool (if there is no wool - a clean towel), tightly bandaged. Flattened a patch quickly thrombosing veins, and bleeding stops. If compressive bandage gets wet, press down firmly on her palm.
To stop the arterial bleeding, you need to pinch the artery.

Technique clamping artery: strongly press the artery with your fingers or fist to the underlying bone formation.
Arteries are easily accessible to palpation, so this method is very effective. However, it requires the person providing first aid, physical force.
If the bleeding has not stopped after the imposition of tight bandage and clamping the artery, apply a tourniquet. Remember, this is a last resort when other methods do not help.
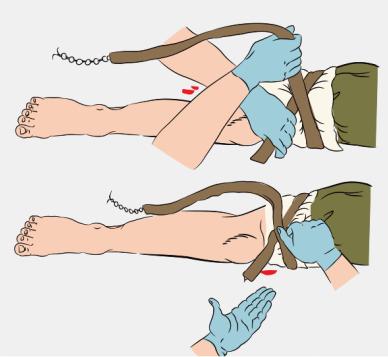
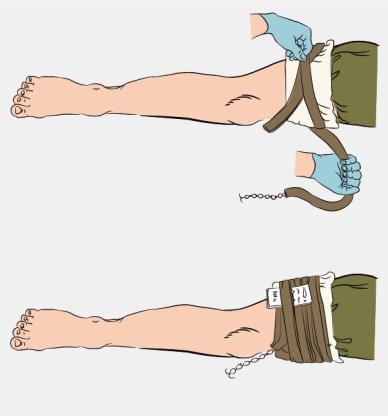
Technique tourniquet
- Tourniquet on clothing or soft cloth slightly above the wound.
- Tighten the harness and check the vessel pulsation: the bleeding must be stopped, and the skin below the tourniquet - blanch.
- Apply a bandage on the wound.
- Record the exact time when the tourniquet.
Tourniquet on a limb, you can apply a maximum of 1 hour. Upon its expiry, loosen the tourniquet on for 10-15 minutes. If necessary, tighten again, but no more than 20 minutes.

fractures
Fracture - a violation of integrity of the bone. Fracture accompanied by severe pain, sometimes - syncope or shock, bleeding. Distinguish open and closed fractures. The first is accompanied by injury of soft tissue in the wound is sometimes visible bone fragments.
Equipment first aid in fractures
- Please rate the severity of the condition of the victim, determine the localization of the fracture.
- If there is bleeding, stop it.
- Determine whether the movement possible victim until the arrival of specialists.
Do not move the victim and did not change its position in spinal injuries!
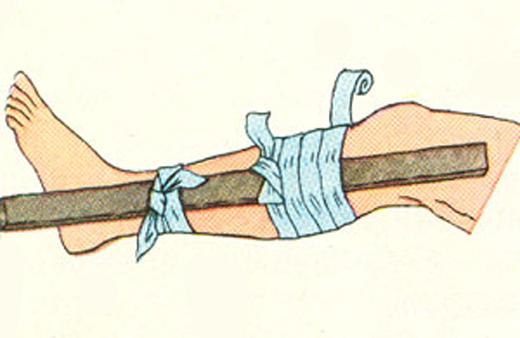
- Provide bone stiffness in the field of crisis - conduct immobilization. For this it is necessary to immobilize the joints above and below the fracture.
- Splint. As tires are flat, you can use sticks, boards, lines, bars and so on. Bus must be tight, but not tight to fix the bandage or plaster.
In a closed fracture immobilization is made on top of clothing. When open fractures can not be applied to the bus places where bone protrudes outward.


burns
Burn - this damage body tissues at high temperatures or chemicals. Burns vary in degrees, as well as damage types. According to the latest release base burns:
- thermal (flame, hot liquid, vapor, incandescent material);
- chemical (alkali, acids);
- electrical;
- ray (light and ionizing radiation);
- combined.

In case of burns the first step is to eliminate the damaging factors (fire, electric current, hot water and so on).
Then, with thermal burns, the affected area should be released from clothing (gently without tearing off and clipping adhering tissue around the wound) and in order to disinfect and irrigate it analgesia vodospirtovym solution (1/1) or vodka.
Do not use oily ointments and fatty creams - fats and oils do not reduce the pain, do not disinfect the burn and promote healing.
After irrigate wound cold water, apply a sterile dressing and apply cold. Also, give the victim a warm salted water.
To speed up the healing of lung burns, use sprays with dexpanthenol. If the burn covers an area more than one palm, be sure to consult a doctor.
Fainting
Fainting - a sudden loss of consciousness due to a temporary disturbance of cerebral blood flow. In other words, the brain signal that it lacks oxygen.
It is important to distinguish between normal and epileptic swoon. First, as a rule, preceded by nausea and dizziness.
Presyncope characterized by the fact that the man rolls his eyes, covered in a cold sweat, his weakening pulse, limbs are cold.
Typical situations occurrence of syncope:
- fright
- excitement,
- stuffiness and others.
If a person has fainted, giving it a comfortable horizontal position and provide fresh air (unfasten clothes, loosen the belt, open windows and doors). Drizzle on the victim's face with cold water, pat him on the cheeks. In the presence of first-aid kit on hand give a sniff cotton swab dipped in liquid ammonia.
If consciousness is not returned 3-5 minutes, immediately call an ambulance.
When the victim wakes up, give him a strong tea or coffee.
Drowning and sunstroke
Drowning - is the penetration of water into the lungs and respiratory tract, which can lead to death.
First aid for drowning
- Remove the victim from the water.
Drowning man grasps at everything that will fall under the arm. Be careful: swim up behind him, keep his hair or armpits, keeping the face above the water surface.
- Place the victim on his stomach on knee to the head on the bottom.
- Clean the oral cavity from foreign bodies (mucus, vomit, algae).
- Check for signs of life.
- If there is no pulse and respiration immediately proceed to the ventilation and chest compressions.
- After the restoration of breathing and heart activity, place the affected side, cover it and provide comfort to the arrival of medics.

In summer danger are also sunstroke. Sunstroke - a breakdown of the brain, caused by prolonged exposure to the sun.
symptoms:
- headache,
- weakness,
- noise in ears,
- nausea,
- vomiting.
If the victim is still remains in the sun, he had a fever, shortness of breath and sometimes he even loses consciousness.
Therefore, when first aid is first necessary to move the victim to a cool ventilated area. Then release it from the clothes, loosen the belt, razuyte. Put him on the head and neck with a cold wet towel. Give to smell ammonia. If necessary, give artificial respiration.
When sunstroke victim must be abundantly drink cool, lightly salted water (to drink often, but in small sips).


Hypothermia and frostbite
Subcooling (hypothermia) - a reduction of the body temperature below normal, required to maintain normal metabolism.
First aid for hypothermia
- Get (, store) the victim into a warm room or wrap up warm clothing.
- Do not rub the affected, let the body gradually warm themselves.
- Give the victim a warm drink and a meal.
Do not use alcohol!


Subcooling is often accompanied by frostbite, i.e. the damage and necrosis of body tissue under the influence of low temperatures. Particularly common frostbite of the fingers, toes, nose and ears - parts of the body with a reduced blood supply.
Reasons for frostbite - high humidity, frost, wind, fixed position. It aggravates the condition of the victim, as a rule, alcoholic intoxication.
symptoms:
- feeling cold;
- tingling of parts of the body frostbite;
- then - numbness and loss of sensation.
First aid for frostbite
- Place the victim in the heat.
- Remove its promorzshuyu or wet clothes.
- Do not rub the affected snow or cloth - so you only injure the skin.
- Wrap frostbitten area of the body.
- Give the victim a sweet hot drink or hot food.


Poisoning
Poisoning - is a disorder of the body of life, which arose due to being hit by poison or toxin. Depending on the type of toxin poisoning are distinguished:
- carbon monoxide,
- pesticides,
- alcohol,
- drugs
- food and others.
The nature of the poisoning depends on first aid measures. The most common food poisoning, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and stomach pains. Affected in this case recommended to take 3-5 grams of activated charcoal every 15 minutes for an hour, drink a lot of water, refrain from eating and be sure to refer to the doctor.
In addition, the common accidental or intentional poisoning of drugs, and alcohol intoxication.
In these cases, first aid consists of the following steps:
- Wash the affected stomach. To do this make him drink several cups of salted water (1 L - 10 g of salt and 5 g of sodium hydroxide). After 2-3 glasses call the victim vomit. Repeat these steps until the vomit will not be "clean."
Gastric lavage is only possible if the patient is conscious.
- Dissolve in a teacup 10-20 charcoal tablets give drink is affected.
- Wait for the arrival of specialists.

