How different types of exercise affect our brain
Health / / December 19, 2019
Brain and physical activity: a direct relationship
To build muscle, you need to drag the iron. Yoga develops flexibility and helps to relax. Running eliminates the excess centimeters at the waist and is one of the fastest ways to lose weight and tighten the body. Various fitness trends to help us get healthy and focused, to create the perfect body. They are something of a power bomb and uplifting.
Thanks to recent research we can develop the brain in the desired direction as well as the body. Various physical differently affect the exercise not only the body but also the brain: each of them activate the specific site.
Physical activity makes us smarter, delays approaching senility, helps fight depression and Parkinson's disease. This is due to the fact that blood saturated with oxygen, hormones and nutrients quickly to the brain. All this makes it the same healthy, efficient and strong as the heart and lungs.
Scientists decided to find out which areas of the brain is influenced by high-intensity interval, aerobic and strength training, yoga, and other exercise facilities.
Does it make sense to accelerate or, on the contrary, it is better to slow down? Go to the gym to weight training or yoga? It all depends on the goal that you are pursuing: to become more focused before an exam or a complex work, relax, or to quit smoking.
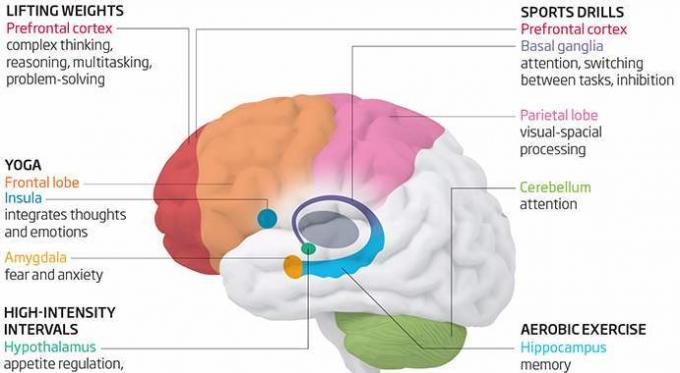
Effect of exercise on memory and executive functions
aerobic exercise
Guesses about the impact of specific types of exercise on the brain appeared 15 years ago, thanks to experiments on rodents. Scientists found that mice who are actively spinning wheel, to form new neurons in the hippocampus - a brain region responsible for memory. Exercises made hippocampal neurons to pump a special protein - brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), contributing to the formation of new neurons. In the experimental mice in the experiment improved memory, allowing them to be easier to navigate through the maze.
Soon after the study was postponed to a person.
Older people who performed aerobic exercise three times a week throughout the year, improved memory. In their blood had a higher level of protein BDNF, and the hippocampus was observed more active formation of new neurons.
Conclude that jogging and aerobic activity to help fight senile dementia and Alzheimer's disease are prevention, it has become good news. Search for other methods of treatment and prevention of many cognitive impairment progressed rather slowly, and existing drugs have unpleasant side effects.
strength training
Teresa Liu-Ambrose (Teresa Liu-Ambrose) from the University of British Columbia (Canada) decided to go ahead and cover it in more detail. She wanted to find out which parts of the brain is affected by certain exercises, and was looking for ways to slow the progression of dementia in people with cognitive impairment. In the process, Teresa Liu-Ambrose particularly interested in the influence of strength training.
To test their idea, Teresa Liu-Ambrose conducted a study involving 86 women with mild cognitive impairment, and compared the effect of aerobic exercise with strength training. Teresa assess their impact on memory and executive functions, which include complex thought processes (reasoning, planning, problem solving and multi-tasking).
One group of subjects twice a week for an hour engaged in strength training, while the second group was walking briskly to give sufficient load. The control group was engaged only in stretching.
After six months of training, the members of the groups that are engaged in strength training and fast walking, an improvement in spatial memory - the ability to remember the environment and its place in the her.
Each exercise had its beneficial effects.
The members of the group, which was engaged in weight training, there were significant improvements of executive function. They also showed the best results in tests on associative memory, which is typically used to communicate ideas and circumstances with each other.
People who perform aerobic exercise significantly improved their verbal memory, ability to learn and to find the right words.
Subjects who engaged exclusively in stretching, showed no improvement in the development of memory and executive functions.
Combining different types of activity
If the benefits of strength training and aerobic exercise are different, that is, if you combine them?
To solve this problem Bozers William (Willem Bossers) from the University of Groningen (Netherlands), divided 109 people with dementia into three groups. One group went out for a 30-minute walk briskly four times a week. Combination Group had a half-hour walking tours twice a week. In addition, twice a week, people from this group came to weight training. In the control group did not exercise.
After nine weeks Bozers conducted comprehensive testing that is possible to measure the participants' ability to solve the problems of the experiment, the inhibition (inhibition) and the speed of data processing. After processing the results, he found that the combination group showed better results compared with aerobic and control groups.
From the research results it can be concluded that to improve cognitive health of older people is not enough just to go for a walk. They need to add to your calendar a couple of strength training.
Improving concentration
The positive effects of exercise are not confined to those who have problems, but also in healthy adults. After a year of experiments with healthy older women Teresa Liu-Ambrose found that strength training at least once a week, leading to significant improvements in executive function. on balance exercises and simply toning exercises did not give such an effect.
The combination of strength training is aerobic ideal one, since work with weight releases insulin-like growth factor - 1 (IGF-1) - growth hormone, which is produced in the liver. He is known for his influence on the relationship between brain cells and promotes the formation of new neurons.
Moreover, aerobic exercise increases protein production BDNF, weight training and reduce the level of homocysteine - an amino acid, the amount of which is increased in the brains of elderly people with dementia.
Combining strength and aerobic workout, you get a powerful neurobiological cocktail. Unfortunately, the study did not specify the duration of the healing effect of exercise, but quite clearly indicate that to maintain the mental health of older people should train.
Other studies show how different exercises affect the development of the child and ability. For example, if you want your child to be focused even for an hour, it is best to allow him to run a couple of laps. A twenty-minute walking has immediate positive effect on the children's attention and executive functions. Running and dancing have roughly the same effect. Walk briskly also helps to focus on the task at hyperactive children with attention deficit.
Exercises that focus on the development of any specific skills (for example, coordination of movements), impair attention. A large number of rules and special exercises may be too difficult for children, especially before tests or in situations that require concentration. However, these exercises have a positive impact on the development of concentration in the long term.
Maria Chiara Dzhalotta (Maria Chiara Gallotta) from the University of Rome (Italy) found that those with complex games coordination of movements, like basketball or volleyball help children better take tests that require concentration.
Cerebellum - a brain region that is not only responsible for the coordination of movement, balance and regulation of muscle tone. He is also involved in the concentration. Testing of complex movements activates the cerebellum, which interacts with the frontal lobe increases attention.
Moreover, the children involved in sports, the hippocampus and the basal ganglia are larger than those of inactive children. These children are more attentive. Basal ganglia are a group of structures that play an important role in the movement and goal-directed behavior (turning ideas into action). They interact with the prefrontal cortex and the impact on attention, executive control and braking, helping people to switch between two tasks.
Adults can also benefit from the execution of complex tasks of sports. Research conducted in Germany showed an increase in the basal ganglia volume after such exercises on coordination, as the retention of balance, synchronization of movements of arms and legs. The same effect was observed when using cords and balloons.
synchronization exercise improves visual-spatial processing information needed to determine the distance in mind. For example, it may be time to estimate the road junction before the red light.
Another explanation set forth in the studies conducted Tracy Alloway (Tracy Alloway) and Rose Alloway (Ross Alloway) at the University of North Florida (USA).
Scientists have found that a couple of hours of such activity as climbing trees, balancing on the crossbar or running barefoot, have a significant effect on memory.
RAM is responsible for the ability to hold information in mind and manipulating it at the same time. It processes the information and decide what is important, ignoring the fact that it is not related to the work you are doing at the moment. RAM affects almost everything you do.
What is special about climbing trees or balancing on the bar? The researchers found that only the combination of two different activities gives positive results. Both options in this case include a sense of proprioception (sense of position of his body parts relative to each other in space).
It must also be present another element - calculation of the distance to the next point, navigation or moving in space. The positive effect will be the exercise in which you want to move, and at the same time to think where and how to do it.
control of appetite
One of the latest fashion trends in sports - High intensity interval training (HIIT), which include exercise with alternating high and low intensity loads. These short workouts provide the same benefits as the more familiar long-term employment.
Do interval training has its advantages: short bursts of activity reduce the feeling of hunger.
To test the effect of interval training on appetite, scientists from the University of Western Australia invited the men who are overweight to participate in the experiment. Scientists asked subjects for three days to ride a bike 30 minutes. The intensity of the training had to be different each time. On the fourth day, the subjects were resting.
It turned out that after the most intensive training and during the remaining time before sleep men ate less than usual. Moreover, their appetite for the next few days was twice less than in the days after exercise of moderate intensity, and after a day of rest.
One explanation for this phenomenon may be that exercise lowers the level of ghrelin - the hormone of hunger. He is responsible for the message to the hypothalamus - the part of the brain that controls the feeling of satiety, and lets you know when the stomach is empty. As soon as the stomach is filled, the production of ghrelin stops hunger disappears. After high-intensity training ghrelin levels in the body was the lowest.
results
So, what to remember from this mass of research for those who want to pump the brain by means of physical exercise?
- Jogging and aerobic activity to help fight senile dementia and prevent Alzheimer's disease, improve verbal memory, ability to learn and to find the right words.
- Strength training is a positive influence on the executive functions of the brain, that is, planning and regulation of conscious actions.
- Games with a complex coordination of movements helps children concentrate better.
- Interval training allows to control appetite.
- The greatest positive effect for the brain can be achieved by combining different kinds of activities, such as aerobic and power loads.



