What is eczema, why does it appear and how to treat it
Educational Program Health / / December 30, 2020
What is eczema
Eczema is the most common type of dermatitisEczema (A to Z), that is, inflammatory skin diseases. Every fifth person encounters her at least onceAtopic dermatitis (eczema) child and every thirty adults. It is not dangerous, but it can seriously reduce the quality of life.
The Greek verb eczeo, which gave the name to this disease, means "to boil." With typical eczema, dozens of tiny bubbles filled with liquid seem to boil on the affected area of the skin. They itch, tingle, burn. After a day or two, they break and dry out, leaving irritated flaky skin underneath.
See what eczema looks like.
Hide.
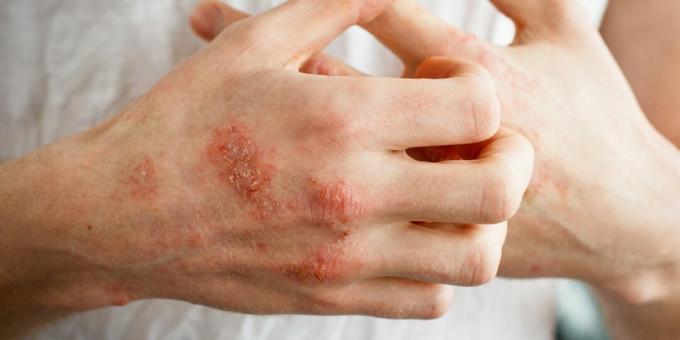
The unpleasant symptoms of eczema often disappear after a week or two. But they can last for years. In this case, they say that the disease has become chronic.
Eczema is sometimes called atopic dermatitis. But this is not entirely correct. "Atopic" meansAtopic "Caused by allergies". This is the most popular form of eczema, but there are others.7 types of eczemaappearing for other reasons.
Reading now🔥
- 8 signs of myocardial infarction that require an ambulance call
What are the types of eczema
1. Atopic dermatitis
This type of eczema, as a rule, occurs at an early age and haunts a person throughout his life, sometimes reminding himself, then disappearing. Atopic dermatitis is part of the so-called atopic triad, which, in addition to eczema, includes asthma and hay fever (seasonal allergies). Many people who suffer from allergic eczema have all three conditions.
Doctors suggest that atopic dermatitis is associated with genetics and may be hereditary.
Most often, this type of eczema occurs:
- on the hands;
- in the bends of the knees and elbows;
- on the ankle;
- on the upper eyelids, ears;
- on the cheeks (in children).
2. Contact dermatitis
In this case, the appearance of a rash is associated with a reaction to substances or objects that you touch. The most common irritants are:
- detergents, including bleaches;
- skin care products, including decorative cosmetics;
- soap and perfumery;
- jewelry;
- latex;
- nickel;
- dyes;
- poison ivy or other toxic plants;
- solvents;
- tobacco smoke.
3. Dyshidrotic eczema
Itchy blisters appear on the fingers, palms, and soles of the feet. It is believed that this type of eczema is caused by a combination of factors - in particular, personal reaction to stress and sweating of the skin on the hands and feet.
Dyshidrotic dermatitis is more common in women.
4. Hand eczema
This type of dermatitis only affects the palms and hands. In part, hand eczema is similar to contact dermatitis: it often occurs in those who work with chemicals that irritate the skin, such as cleaning, laundry, or hairdressing salon.
However, hand eczema can also occur when exposed to cold and dry air in winter.
5. Neurodermatitis
Doctors associate the manifestations of this type of eczema with a reaction to psycho-emotional stress, although this is not accurate. As a rule, neurodermatitis occurs in those who are predisposed to skin diseases and have already encountered other types of eczema or psoriasis.
6. Nummular eczema
With this type of disease, rounded spots the size of a coin appear on the skin (the word nummular in Latin means “coin”). Nummular itching can be especially severe.
Coin dermatitis is often caused by bites insects or an allergic reaction to metals or chemicals. However, even dry skin can provoke its appearance.
7. Stasis-dermatitis
He's also congestive dermatitis. This eczema occurs on the feet and legs. It is caused by circulatory problems in the lower legs.
Stasis-dermatitis often occurs in those who suffer from edema and varicose veins lower limbs.
How to treat eczema
It depends on what exactly is causing the rash. For example, atopic dermatitis, especially in young children, is often associatedEczema with the use of some products - eggs, milk, soy, wheat, strawberries, citrus fruits, chocolate. To reduce irritation, it is enough to adjust the child's diet by removing food allergens from it.
It is best to start the fight against itchy spots and skin rashes with a visit to a dermatologist, in case children - a pediatrician. The doctor will examine you and ask you a few questions to determine the possible causes of eczema. The following may be asked:
- What do you eat and drink? Have you eaten any new foods shortly before the skin irritation started?
- What detergents, soaps, cosmetics do you use?
- What do you do in your free time? Perhaps you like to walk in the woods or meadows (there is a risk of contact with poisonous plants) or swim in a pool with chlorinated water?
- How much time do you spend in the bath or shower? What is the water temperature?
- Are you often nervous?
- Are there people among your close relatives who also suffer from dermatitis?
The doctor may also suggest that you take a test for allergies. A special patch with a small dose of popular allergenic substances will be placed on your skin, and after 20-30 minutes it will be removed and checked for a reaction.
Depending on the results of the examination and test, the dermatologist will prescribe treatment. It may includeEczema:
- corticosteroid ointments or creams to help relieve itching and restore skin
- antihistamine tablets;
- drugs to reduce the immune response that causes redness and itching;
- antibiotics - if, due to the constant scratching of eczema, you have developed a bacterial infection;
- UV baths - In some cases UV radiation can reduce breakouts.
However, you can often do without pills and medicated ointments. Just a little changeEczema lifestyle to ease the condition. These changes will also reduce the risk that the disease will recur.
How to relieve and prevent eczema
1. Moisturize your skin
First of all, this applies to those areas that suffer from eczema: hands, cheeks, legs, feet. Apply a greasy cream, ointment or lotion to them at least twice a day to help your skin maintain normal moisture. It is best to do this after taking a bath or shower.
2. Reduce water treatment time
Try to swim for no longer than 10-15 minutes and use warm, not hot, water.
3. Use only mild, unscented soap
Antibacterial and flavored agents wash away sebum quite aggressively and contribute to dryness of the epidermis.
4. Dry with a soft towel
After bathing, gently pat dry with a soft towel and apply moisturizer while the skin is still damp.
5. Try to identify what causes eczema and avoid those factors
The most common triggers that can trigger dermatitis are:
- some foods (especially important for young children);
- stress;
- unsuitable detergents, soaps, cosmetics;
- sweat;
- chlorinated water;
- pollen of various plants;
- inhalation of house dust, mold - think about this factor if eczema worsens every time, when, for example, you are visiting a relative or spending a few hours in someone else's house or office;
- Jewelry;
- too high or low temperature.
If you can't identify the stimulus straight away, start keep a diary. Record in it what you ate, what you did and where you were. When your eczema flares up, your diary will give you a high probability of guessing what exactly caused it.
Once you find a trigger, try to get rid of it. For example, replace your usual soaps and detergents with milder, hypoallergenic products. Discard some jewelry. Change the pool. Review your eating habits. This will help reduce the frequency of skin irritations.
Read also👩⚕️💊🌡
- Measles: why are they so afraid of it and isn't it better to get sick
- What is mononucleosis and how to treat it
- 10 unexpected reasons why you itch
- Chickenpox in children and adults: how not to get sick and how to be treated
- 13 symptoms of lupus that are dangerous to ignore



