All the secrets of Excel-function CDF (VLOOKUP) to search for data in a table and retrieve them to another
Tips Technologies / / December 19, 2019
Batyanov Denis on the Rights of the guest author explains in this post about how to find data in one Excel spreadsheet and extract them to another, and discovers all the secrets of the vertical viewing function.
When working in Excel very often there is a need to find data in a table and remove them to another. If you do not know how to do it, then I read the article, you'll not only learn it, but also find out under what conditions you will be able to squeeze out the maximum performance of the system. Considered most highly effective techniques that should be used in conjunction with the function of the CDF.
Even if you have years of use the CDF function, with high probability this article will be useful to you and will not leave indifferent. I, for example, as IT-specialist, and then the leader in IT, used VLOOKUP 15 years, but to deal with all the nuances happened just now, when I'm on a professional basis I began to teach Excel people.
CDF - an abbreviation of inVertical, etcinspection. Similarly, VLOOKUP - Vertical LOOKUP. The very name of the function suggests to us that it searches the rows of the table (vertical - sorting line and fixing axis), and not in the columns (horizontal - sorting the columns and fixing line). It should be noted that the CDF has a sister - the ugly duckling that will never become a swan - is a function of the PGR (HLOOKUP). PGR, as opposed to the CDF, produces a horizontal search, but the Excel concept (and indeed the concept organizing data) means that your tables have a small number of columns and many more lines. That is why the search for strings, we need many times more than the columns. If you
Excel too often use HLOOKUP, it is quite likely that there is something you do not understand in this life.Syntax
VLOOKUP has four parameters:
PPS = (
I bet that many of those who know the CDF function as a peeling, read the description of the fourth parameter may feel uncomfortable because they used to see it in a slightly different way: usually there is a speech about the exact accordance with the search (FALSE or 0), or about the same viewing range (TRUE or 1).
Now it is necessary to tighten and read the next paragraph a few times until you get a feeling for the meaning of what has been said until the end. There is important to every word. Examples will help to understand.
As the same formula CDF works particularly
- Type of formula I. If the last parameter is omitted or specified as 1, the CDF expects that the first column is sorted in ascending order, so the search will stop at the line that immediately precedes the row in which the value greater than the desired. If this line is not found, it returns the last row of the range.
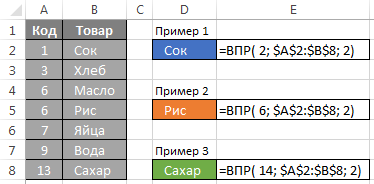
- Type of formula II. If the latter option is specified as 0, then the CDF sequentially scans the first column of the array and immediately stops search when first found an exact match with the parameter
, otherwise an error code is returned # N / A (# N / A). 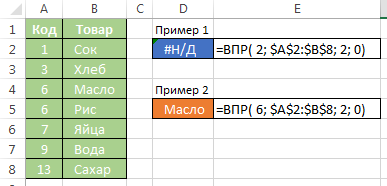
the formulas of the scheme
CDF Type I

CDF Type II

Implications for the species of formula I
- The formulas can be used for distribution of the range of values.
- If the first column
contains duplicates and sorted properly, it will be returned the last of the rows with duplicate values. - If we look for the value obviously more than you can contain the first column, you can easily find the last row of the table, which can be quite valuable.
- This view will return an error # N / A only when it finds a value less than or equal to the desired.
- Understand that the formula returns an incorrect value, if your array is not sorted, quite difficult.
Implications for the species of formula II
If the value is found in the first column of the array several times, the formula will select the first row for later retrieval.
Productivity VLOOKUP
You have reached the climax of the place of the article. It would seem, well, what's the difference if I point out as the last parameter zero or one? Basically, all the point, of course, zero, as it is quite practical: no need to worry about sorting the first column of the array, one can see, found the value or not. But if you have a list of several thousand formulas CDF (VLOOKUP), you will notice that the CDF type II runs slowly. It is usually all start to think:
- I need a more powerful computer;
- I need a quick formula, for example, many people know about the INDEX + MATCH (INDEX + MATCH), which is supposedly faster miserable 5-10%.
And few people think that as soon as start using the CDF type I and provide any way to sort the first column as the speed of the CDF operation will increase 57 times. I write words - In FIFTY SEVEN TIMES! In 57% and 5700%. This fact I checked quite reliably.
The secret to such quick work lies in the fact that you can apply to the sorted array is extremely efficient search algorithm, which is known as a binary search (bisection method, dichotomy). So I kind of CDF uses it, and the CDF type II seeks without any optimization in general. The same applies to the MATCH (MATCH), which includes the same parameter, and also to function WATCHING (LOOKUP), which works only on sorted arrays and activated in Excel for compatibility with Lotus 1-2-3.
disadvantages formula
Disadvantages of the CDF are obvious: first, it seeks only the first column of this array, and secondly, just to the right of this column. And as you know, it may well be that the column that contains the necessary information to the left of the column in which we seek. Devoid of this shortcoming already mentioned a bunch of formulas INDEX + MATCH (INDEX + MATCH), which makes it the most flexible solution to extract data from tables in comparison with the CDF (VLOOKUP).
Some aspects of the application of the formula in real life
Range search
Classic illustration of the search range - the problem of determining the size of the order discounts.

Search for text strings
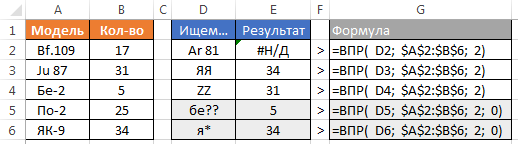
Of course, the CDF seeks not only numbers but also text. It should be borne in mind that the case-sensitive formula does not distinguish. If you use wildcard characters, it is possible to organize a fuzzy search. There are two wildcard "?" - replaces any single character in the text string "*" - replaces any number of any characters.
Fight with spaces
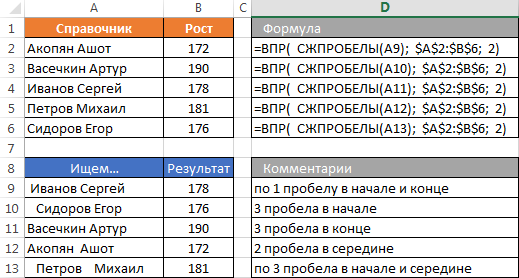
Often the question is raised, how to solve the problem of the extra spaces in the search. If the look-up table is still possible to clean them, the first parameter of the formula CDF does not always depend on you. Therefore, if the risk of clogging the cells extra space is present, it is possible to use the TRIM (TRIM) function for cleaning.
A different data format
If the first parameter function CDF refers to a cell that contains a number, but which is stored in cell as text, and the first column of the array contains the numbers in the correct format, the search will be unsuccessful. The reverse situation. The problem is easily solved by transfer parameter 1 into the required format:
PPS = (- D7; Products $ A $ 2: $ C $ 5;! 3; 0) - if D7 contains the text and the table - numbers;
= CDF (D7 & «»); Products $ A $ 2: $ C $ 5;! 3; 0) - and vice versa.
By the way, to translate the text in number can be several ways, choose:
- Double Negative -D7.
- Multiplication unit D7 * 1.
- Addition with zero D7 + 0.
- The construction of the first degree D7 ^ 1.
Translation of the text produced by coupling with an empty string, which causes Excel to convert the data type.
How to suppress the issuance # N / A
It is very convenient to do with IFERROR function (IFERROR).
For example: = IFERROR (CDF (D7; Products $ A $ 2: $ C $ 5;! 3; 0); «»).
If the CDF will return an error code # N / A, then it will intercept IFERROR substitute and parameter 2 (in this case, an empty string), and If no error occurred, this function will pretend that it is not at all, but only the CDF, restored to normal result.
Array
Often overlooked an array reference is made absolute, and when pulling an array of "floats". Remember that instead of A2: C5 should be used $ A $ 2: $ C $ 5.
A good idea is to place a reference array on a separate sheet in the workbook. It does not get underfoot, and will have stored.
Even more good idea to announcement of the array as a named range.
Many users are used when specifying the structure of the array type A: C, indicating the columns entirely. This approach has a right to exist, since you are spared from having to keep track of the fact that your array contains all the strings. If you add a line on a piece of the original array, the range specified as the A: C, will not have to adjust. Of course, this syntax causes Excel to spend a bit more work than with the exact indication of the range, but the data overhead is negligible. We are talking about hundredths of a second.
Well, on the verge of genius - to issue in the form of an array smart table.
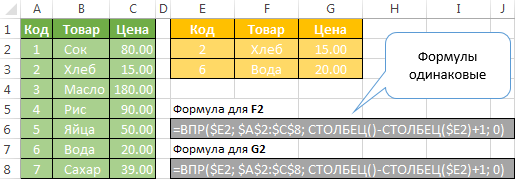
Using COLUMN function for specifying extraction column
If the table into which you extract the data using the CDF, has the same structure as the look-up table, but just comprises a minimal number of rows in the WRT domain can be used COLUMN () function for automatically calculating the numbers of recoverable columns. In this case all the CDF-formula will be the same (adjusted for the first parameter, which changes automatically)! Note that the first parameter is the absolute coordinate of the column.
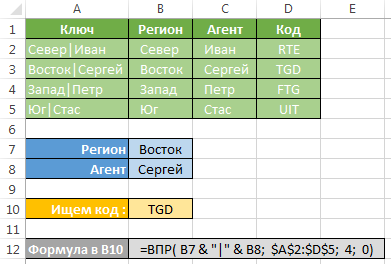
Creating a composite key by & »|» &
If there is a need to look at more than one column at a time, it is necessary to make a composite key for the search. If the returned value is not text (as here in the case of the field "Code"), and numeric, for the This came to a convenient formula SUMIFS (SUMIFS) and an integral key column would not be required at all.
This is my first article for Layfhakera. If you liked it, then I invite you to visit my siteAnd gladly read your comments about the secrets of using VLOOKUP and the like. Thanks. :)

