5 non-obvious ways to spy on you while using a smartphone
Technologies / / December 19, 2019
You probably know that your smartphone can easily be used against you. Cracking a gadget, you can access its camera or microphone. So, everything that you shoot and you say, may be transferred to third parties. The possibilities of modern smartphones are not limited to espionage. In theory, there are a number of other less obvious ways to get information about where you are and what you are doing right now.
1. Keylogger based on data from the gyroscope

All modern smartphones are equipped with a gyroscope. This sensor is needed to determine the exact direction of the tilt of the gadget that can be used to automatically activate any functions or driving a car in a racing game.
Each year these sensors are becoming more accurate. Theoretically, their sensitivity to the slightest variations can be exploited against you. This provedSingle-stroke language-agnostic keylogging using stereo-microphones and domain specific machine learning. Researchers at Northeastern University in Boston. With the help of a gyroscope and microphone they managed to create a fairly accurate keylogger.
Keylogger or a keylogger - a software or hardware device that records various user actions: keystrokes, movement and clicking the mouse gestures touch screen.
When you use the onscreen keyboard, your smartphone whenever you touch a little leans. Recognizing the slightest offset by a gyroscope, a keylogger can guess the sample text that you type. Possible variations are corrected taking into account the intensity of the sound to be emitted when the display window is touched. With this already helping smartphone microphones. Using a combination of sensors and a set of algorithms, researchers from the first time succeeded in guessing keystrokes to within 90-94%.
2. Positioning without GPS
Even when the GPS to determine location of the device It can be used on cell towers and Wi-Fi hotspots with attached thereto geolocation information. However, to obtain information about the user's location can be even without access to such data.
All the same group of researchers from Northeastern University triedSingle-stroke language-agnostic keylogging using stereo-microphones and domain specific machine learning. this is demonstrated by smartphone sensors, which use applications can without special permits. The result of their work was the program employs a gyroscope, accelerometer and magnetometer.
Taking the map of the area in which there was a man, the app allowed to monitor all movements of the vehicle. The accelerometer is used to detect motion and stops. Magnetometer recorded direction. Gyro measured the angles of rotation, allowing to accurately track when and in which direction the car is turning.
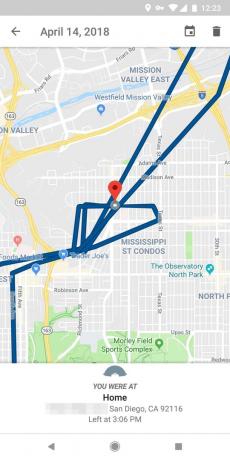
A special algorithm combined data from all of these sensors and formed thereon an exemplary movement pattern. It was compared with the real routes in the area where the wire shadowing. According to these data it is possible to determine exactly where and when the user is driving, how much time he spent on it.
3. Tracking through advertising banners
There is another way to determine the location of a person with no direct access to the data of its GPS-smartphone. This method is described the Washington University researchers, who used banner ads for mobile. The minimum deposit for placing such ads with Google AdWords and Facebook has made 1000 dollars.
When buying a banner, you can specify which application and for any unique identifiers need to display devices. The researchers also pointed out trohmilnuyu square geofence, while in which in the chosen application displays advertising.
Each time the target phone using the specified application, device information, time and place of its finding set off a banner holders. Using this information, the research team was able to track the user's location within 25 feet (~ 7.6 m). However, it is possible, as long as the application remains open for four minutes, or it ran twice in the same place.
Of course, this method requires constant surveillance use a particular application. In part, this obstacle can be avoided if to place banners in the most popular programs. It is also necessary to know in advance the specific advertising device identifier specific person. But even without it, this method may well be used to monitor the population of the selected locations.
4. View visited links via light sensor
Ambient light sensor adjusts the brightness of your screen smartphone. You'd be surprised, but even this seemingly innocuous sensor can be used against you.
Lukasz Olejnik (Lukasz Olejnik) is graphically illustratedStealing sensitive browser data with the W3C Ambient Light Sensor API.By creating an application that according to the light sensor determines the color of the links visited by the user. Simply put, the light emitted from your screen, can be accurately detected by this sensor. This allows you to determine which web page you navigate.
Web sites can display different colors for links. For example, text can be light blue, if you have not visited it before, but it becomes violet after the first press. The site itself is, of course, can not recognize what color a link is displayed for a particular user, for transitions fixes browser. However, if the representatives of the web resource access data light sensor of your smartphone, they light emanating from the screen can determine whether you passed previously on display or link not.
This is especially noticeable on the pages contrasting with a dark background and light text of a hyperlink. Once you stumble upon them, as the sensor detects an increase in the light of the screen. In theory, this way without your knowledge, you can create a list of all the pages you visit.
5. Identification of users and nearby objects
The vast majority of smartphones have the proximity sensor. It was he who used to turn off the touch screen when you call. Otherwise, during a call, you would face continued to press the buttons on the display.
This sensor not only detects that the objects are close to the screen, but also can measure the distance to them. Each of us holds a smartphone at different distances depending on the height, the length of the hands, eyes and other factors. On the basis of this information the application may well differentiate users and their behavioral characteristics.
The accuracy of this method may be low, but in combination with the same target mobile banners, advertisers can identify your target audience. Furthermore, by using the proximity sensor can determine the distance to nearby objects surrounding the user. And it may be more fire under surveillance without using GPS.
Each of these methods is described as yet theoretical. So far, none of them is not widely used. However, it is possible that it is only a matter of time.
see also
- Guide for the paranoid: how to avoid surveillance and data theft →
- As smartphones are watching us and how it threatens →
- Insecure communication: 9 ways to listen to your phone →



