What is tubo otitis and how to get rid of it
Miscellaneous / / April 13, 2021
This disease can go away without treatment. If you're lucky.
What is tubo-otitis
Tubo-otitis is an inflammation of the lining of the auditory tube that connects the middle ear to the pharynx. These tubes (there are two of them, one in each ear) are also called Eustachian tubes. Hence the second name for tubo-otitis - eustachitis.
Important note: both of these terms are used mainly by domestic doctors. There are no such diseases in the International Classifier of Diseases (ICD-10). But there is2021 ICD ‑ 10 ‑ CM Diagnosis Code H68.0. Eustachian salpingitis salpingitis, or in the Russian versionH68.0. Inflammation of the auditory [Eustachian] tube inflammation of the auditory (Eustachian) tube.
Western doctors considerEustachian tube dysfunction tubo-otitis as one of the dysfunctions of the auditory tubes. Dysfunction is said to be because the Eustachian tube cannot perform its main tasks during inflammation. Here they areEar Infection:
- Equalization of pressure in the middle ear cavity. For example, when you take off on plane (or taking a high-speed elevator), the air pressure around you decreases. This causes the eardrum to bend towards the ear canal. With the help of the Eustachian tube, the pressure is quickly equalized and the eardrum returns to its natural, non-bent position.
- Ventilation. The intake of fresh air slightly dries up the natural secretion that is secreted by the glands of the mucous membrane of the middle ear. Due to the decrease in moisture in the ear, bacteria do not multiply so actively.
- Natural drainage. Through the Eustachian tube, excess fluid accumulating in the middle ear is excreted through the nasopharynx.
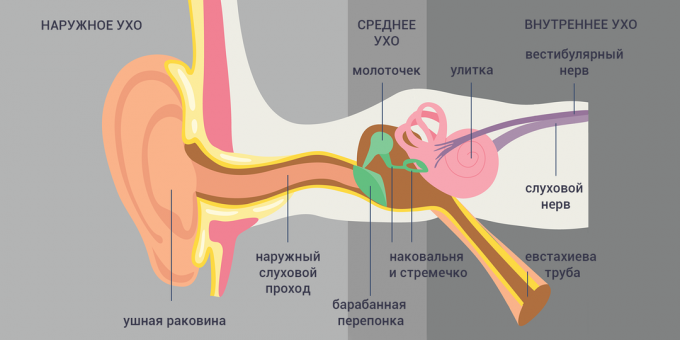
The auditory tube has a very small diameter, literally a couple of millimeters. Due to inflammation, it narrows, becomes blocked. Fluid begins to accumulate in the middle ear, and this can lead toEar Infection to the development of a serious ear infection - medium otitis media.
What are the symptoms of tubo otitis
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube can be assumed by such signsEustachian tube dysfunction:
- Bursting sensation in the ear.
- Ear congestion.
- Hearing impairment.
- Tinnitus. This symptom is called tinnitus.
- Pain in the affected ear.
- Clicking, popping, or itchingWhat You Should Know About Eustachian Tube Dysfunction in the ears.
Where does eustachitis come from
The most common cause of inflammation is an infection that ascends into the Eustachian tube from the mouth or nasopharynx. Therefore, tubo-otitis is often a complication of ARVI or, for example, sore throats.
In addition, inflammation of the auditory tube can lead to:
- Sudden pressure drops. You can encounter them during takeoff or landing of an airplane, scuba diving, ascending on a high-speed elevator.
- Allergy. When an allergic reaction occurs edema mucous membranes, including the Eustachian tube may suffer.
Who has tubo-otitis more often?
The risk groups for physicians includeEustachian tube dysfunction:
- ChildrenEar Infection. Their Eustachian tubes are horizontal and narrower than in adults. Therefore, mucus accumulates there more easily and bacteria begin to multiply.
- Allergy sufferers. That is, people who are more likely than others to develop allergic reactions. They may produce mucus more actively.
- Those who smoke. Smoking damages the protective hairs (cilia) in the middle ear. This increases the risk of mucus accumulating in the Eustachian tube.
What to do if you suspect eustachitis
Tubo-otitis is a harbinger of acute otitis media. Therefore, if the discomfort in the ear does not go away within 24 hoursEar Infection and even more so if the pain itching, the oppressive sensation intensifies, you need to consult a doctor - a therapist or an otolaryngologist.
The doctor will ask you about the symptoms: how well you hear, how severe the pain is, whether there is a temperature, whether there is discharge from the ear. He will conduct an examination: he will look into the external auditory canal and nasopharynx to find out if there is an infection there.
It is possible that ear congestion and pain are caused by waxy plug or accidental water ingestion. The doctor's task is to establish an accurate diagnosis.
How to treat tubo-otitis
If inflammation of the Eustachian tube is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe treatment. What it will be depends on the degree of inflammation and on what caused the eustachitis.
For example, if tubo-otitis is the result of an allergic reaction, the doctor will select antihistamines. With pronounced pain, she will recommend pain relievers, for example, based on paracetamol or ibuprofen (they also have an anti-inflammatory effect). If we are talking about bacterial infectionyou may be prescribed antibiotics. But this is optional.
Ear infection symptoms often resolve on their own within a couple of days. And the disease itself ends in 1-2 weeks without any therapyEar Infection.
However, the decision on how to treat tubo-otitis in your case can only be made by a qualified doctor. Only he knows how high the risk of complications is and how they can be prevented.
Read also👂💊❓
- What to do if a child's ear hurts
- How to understand that you have a plug in your ear, and how to get rid of it
- Where does tinnitus come from and what to do with it
- What to do if it shoots in the ear
- What to do if your ear is blocked