In what format is better to listen to music. Three Pillars lossy
Music / / December 19, 2019
Crazu reservation that article spoke only on the general characteristics and will include some of the details. In the future Layfhaker conduct an impartial investigation of its own. And now we try to summarize already somehow known experience.
There are analog and digital.
Analogue - good, but short-lived and embarrassing. Therefore, analog media, despite the high sales of vinyl, will not return.
Audiotsifra can be of three basic types:
- in a format that does not use compression;
- format employing lossless compression (lossless);
- in a format that uses lossy compression (lossy).
At first glance, more promising formatsUsing lossless compression. This is not always the case, as we will describe in detail one of the following materials. Formats without compression do not have any meaning other than the storage of master recordings needed to create audio content. They are easier to restore. For storing and listening to home recordings are unnecessary.
From the set of parameters of the digital audio user must first excite the sample rate (precision digitizing analog signal in time), capacity (accuracy of digitizing the amplitude - the volume), the bit rate (the amount of information contained in the file in terms of give me a sec).
Today let's talk about lossy.
Compressed audio is very important to the concept of the psychoacoustic model - representation of scientists and engineers on how a person perceives sound. The ear perceives the entire spectrum of incoming acoustic waves to it. However, the brain processes the signals.
Reference value of human hearing range is from 16 Hz to 20 kHz, but simultaneously hear and understand all incoming sounds he can not.
The rumor is discrete, and its sound is nonlinear susceptibility.
Advanced psychoacoustic model estimate fairly accurately the human hearing and are constantly improving. In fact, despite the assurances of music lovers, musicians and audiophiles, for the average untrained initial appearance hearing in the highest quality MP3 became very perceptible. There are exceptions, they can not be. But they are not always easily visible when blind audition.
Formats using psychoacoustic model Compression
Such formats for audio compression losses are many. The most common today.
OGG (Vorbis)
Generally, a file with the extension * .ogg is a "container": inside can be several sound recordings with their own tags and features. Most often stored in it files compressed codec Ogg Vorbis, although can be used and others, including an MP3 or FLAC.
As its main advantages is called a large range of possible settings while encoding: sampling frequency sound can reach 192 kHz word length - 32 bits. Default OGG uses variable bit rate (although when displaying the properties is not indicated), which can be up to 1000 kbit / s.
MP3
In contrast to the free OGG, MP3 was developed very important for modern acoustics Fraunhofer Society - Joint Institute for Applied Research in Germany. Among audiophiles, by the way, this is an extremely reputable firm, however, admit they do not like it. But behind them are closely watching developments.
Unlike OGG, can have both a variable (VBR), and constant bit rate (CBR). By the way, thanks to MP3 discovered that not every entry can be qualitatively encoded with variable bit rate (causes See above, encoding algorithms and the results in this case may be different in encoding same source).
In view of the elderly MP3 has significant limitations: the bit can be 16-24 bit rate Sampling is expressed only in discrete values (8, 11.025, 12, 16, 22,05, 24, 32, 44.1, 48), the bit rate is limited 320 kbit / s. In addition to the usual MP3 versions of the number of channels is limited to two.
AAC
The same mistake, only in profile. also to develop Fraunhofer. And later uses a different psychoacoustic model, more modern. Publicly available information leads to the conclusion that yes, they were able to improve their own creation.
Even if you rely on the most simple figures, AAC - a more flexible format. Bit files obtained by means of this design, is from 16 to 24, the sampling frequency also if desired not allow to lose the sound image and is in the range 8-192 kHz. The data stream generally approaching those of lossless-formats (up to 512 kbit / s), while the maximum number of files AAC-channels reaches 48.
What format should be named clearly the best
If we consider that AAC - reinterpreted after ten years of MP3, the choice in his favor. If desired, it makes sense to compare only MP3 and OGG. Let's take a look at the pictures, made with respect for Andrei Aspidovym ixbt.com:
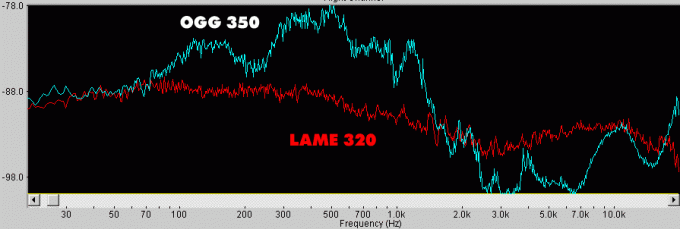
On the charts - a good AudioCD, OGG compressed with variable bit rate of 350 kbit / s, and MP3 using Lame. The lower graph is located, the closer to the original sound. It turns out very interesting picture. Despite the fact that the MP3 has clearly cut high frequencies, unlike OGG, wherein the obstruction seen below 2 kHz.
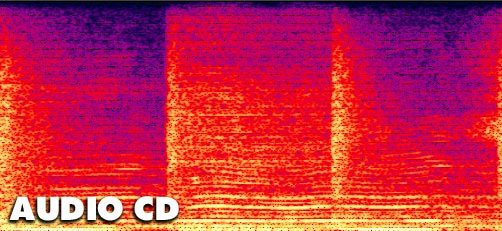
Time-frequency sound distribution shows no less interesting things. At a constant bit rate of 320 kbit / s MP3 is almost identical to the original recording. It seems that now everything falls into place. But... In fact, still more confused.
Why do we use lossy, when there is an available lossless
Common sense.
The fact that the majority of analog records do not contain the amount of data that must be stored in high-quality formats. Do not forget that the native sampling rate for CD is 44.1 kHz, quantization - a total of 16 bits.
Previous charts show good high fidelity MP3. But for audio cassettes, magnetic tape (unless, of course, it is not master teip) AudioCD characteristics unattainable. Yes, and for the mass of studio equipment the ability to record analog sound corresponding to AudioCD, appeared relatively recently. There is no point in digitize FLAC (and especially in WAV) live recording or plate from the pre-digital age, in particular made from magnetic media. They do not contain the spectrum and the amount of information that can be stored without compression containers.
What has changed today
Rare sound engineer makes a digital master record (which then made reproduction on physical media), using modern technology to the fullest. Therefore, the chance that the 24-bit track is actually only 16-bit, is extremely high.
Analog high-quality recording on high-quality equipment to meet today even more difficult - unless fans of this sound. Thus, for example, it is Jack White, the former leader of the band White Stripes. In this part of its records related to variations in the lo-fi, and there seek exorbitant sound characteristics of the track becomes a kind of a treat for gourmets.
If we imagine an ideal source, only a trained ear or listen to high-quality audio equipment will allow to find a compressed file. And based on this (and do not forget about the perception), Should draw the following conclusion:
A necessary and sufficient for the mainstream equipment is AAC, in the absence of which (in the absence of source that can encode in AAC) - MP3 with constant bit rate of 320 kbit / s, created with the help of Lame 3.93 codec (recommended when decoding keys: -cbr -b320 -q0 -k -m s).
The exception is the recording, which was originally produced in high quality, for example, recorded on a DVD-Audio, SACD, or recording, originally collected in the DSD (or similar format) with high bitrate.
Although some features have lossless there. And we will tell about them in the next time.
The author does not like Apple. The author appreciates the achievements of the "Fraunhofer" and was extremely surprised to learn that the AAC - their work. :)

