Lactic acid - a friend of yours, whatever said fitness coach
Educational Program Health / / December 19, 2019
What is lactic acid and lactate
Our body constantly need energy for organs and muscles. With food in the body receives carbohydrates. In the intestine they are broken down into glucose, which then enters the bloodstream and transported to the body's cells, including muscle.
The cytoplasm of cells occurs glycolysis - oxidation of glucose to pyruvate (pyruvic acid) to form ATP (adenosine triphosphate, the main fuel of the organism). Then, due to the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid which immediately loses hydrogen ion, sodium ion may attach (Na +) or potassium (K +) and converted into lactic acid salt - lactate.
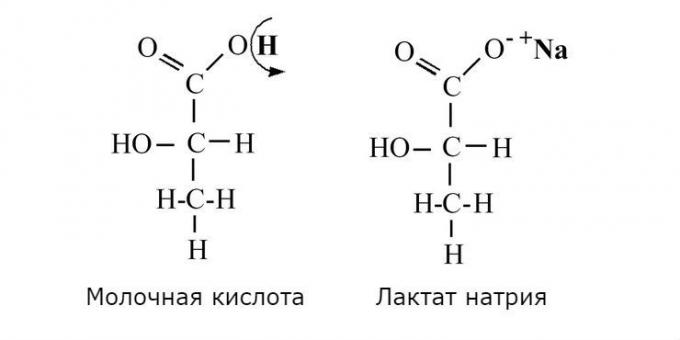
As you can see, lactic acid and lactate - is not the same thing. Accumulates in the muscles, it is displayed and processed lactate. Therefore, to talk about the lactic acid in the muscles properly.
Before 1970, the lactate was considered a byproduct that occurs in the working muscles due to lack of oxygen. However, studies in recent decades have denied the allegation. For example, Matthew Rogatski (Matthew J. Rogatzki) found in 2015
Lactate is always the end product of glycolysisThat glycolysis always ends with the formation of lactate.It also arguesWhat does glycolysis make and why is it important? George Brooks (George A. Brooks) from the University of California who studies the lactic acid more than 30 years. Lactate accumulation shows only the balance between its production and removal and has no relation to the aerobic or anaerobic metabolism.
Lactate always formed during glycolysis, regardless of the presence or lack of oxygen. It is made even at rest.
Why many do not like lactic acid
Myth 1. Lactic acid causes muscle pain
This myth has long been denied, but some fitness trainers still blame lactate in delayed onset muscle soreness, or delayed muscle pain. In fact, the level of lactate is greatly reduced within a few minutes after exercise and completely returns to normal in about an hour after your workout.
Thus, the lactate can not cause muscle soreness 24-72 hours after training. On what mechanisms cause your muscles ache after training, can be found in this article.
Myth 2. Lactic acid "acidifies" muscles and causes them to fatigue
There is a widespread belief that the lactate level in the blood affects the functioning of the muscles. However, in reality this is not fault lactate and hydrogen ions, which increase the acidity of the tissues. When the pH-balance is shifted to the acid side, comes acidosis. There are many studies showing that acidosis has a negative impact on muscle contraction.
In the scientific articleBiochemistry of exercise-induced metabolic acidosis "The biochemistry of metabolic acidosis caused by exercise," Robert Robergsa (Robert A. Robergs) indicates that hydrogen ions are released each time the ATP is cleaved to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate with the release of energy.
When working with moderate intensity, hydrogen ions used for mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (ATP recovery from ADP). When the intensity of exercise and the body's need for energy increases, ATP recovery is mainly due to the glycolytic and fosfagennoy systems. This causes an increased release of protons and, as a result, acidosis.
In such circumstances, it increased production of lactate to protect the body from the accumulation of pyruvate and delivery NAD +, required for the second phase of glycolysis. Robergs suggested that helps to cope with lactate acidosis, because hydrogen ions may migrate from the cell. Thus, without an increased production of lactate acidosis and muscle fatigue would have come much quicker.
Lactate is not to blame for the fact that during the heavy load you are tired muscles. Fatigue causes acidosis - accumulation of hydrogen ions and shifting body pH to the acid side. Lactate, on the contrary, helps to cope with acidosis.
The lactate is good for health and physical fitness
Lactate is a source of energy
In the 80-90-ies Sangiorgi Brooks provedLactic Acid Not Athlete's Poison, But An Energy Source - If You Know How To Use ItThat lactate from muscle cells enters the bloodstream and transported to the liver where it is restored to the Cori cycle in glucose. After this re-glucose is transported by the blood to the working muscles and can be used to produce energy and stored in the form of glycogen.
Moreover, even the muscles can use lactate as fuel. In 1999, Brooks foundLactic Acid Not Athlete's Poison, But An Energy Source - If You Know How To Use ItThat endurance training reduces the level of lactate in the blood, even when the cells continue to produce it in the same amount. In 2000, he found out that endurance athletes increasing the number of molecules of lactate transporters that move quickly lactate from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria of cells.
In further experiments, researchers found within mitochondria, not only proteins, vectors, but the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, which starts conversion of lactate energy.
Scientists have concluded that the lactate is transported into the mitochondria and is burned there with the participation of oxygen for energy production.
Lactate is a source of energy for muscles. In the liver, it is reduced to glucose, which is then used again muscles or stored therein in the form of glycogen. Also, lactate may be burned directly in muscle for energy.
Lactate increases endurance
Lactate helps increase oxygen consumption, which also has a positive effect on endurance. StudyLactate, not glucose, up-regulates mitochondrial oxygen consumption both in sham and lateral fluid percussed rat brains. 2006 showed that the lactate, unlike glucose, increases the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria, which allows them to generate more energy.
And in 2014 it became clearEffect of lactate on intermediary metabolites expression and mitochondrial biogenesis in perfused hearts (864.5)That lactate lowers the stress response and increases the production of genes involved in the creation of new mitochondria.
Lactate increases the amount of oxygen consumed, so your body will be able to carry the load any longer.
Lactate protects the brain
Lactate prevents glutamate-induced excitotoxicity L-. This pathological condition in which due to excessive activity of neurons damaged mitochondria and membranes, and the cell dies. Excitotoxicity can cause multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and other diseases associated with damage to nerve tissue.
StudyLactate Modulates the Activity of Primary Cortical Neurons through a Receptor-Mediated Pathway 2013 proved that lactate regulates the activity of neurons, protecting the brain from excitotoxicity.
In addition, brain lactate provides an alternative power source when glucose is not enough. Also in 2013, scientists foundLactate preserves neuronal metabolism and function following antecedent recurrent hypoglycemia.That a slight increase in circulating lactate allows the brain to function properly in conditions of hypoglycemia.
Moreover, the studyLactate Effectively Covers Energy Demands during Neuronal Network Activity in Neonatal Hippocampal Slices. 2011 showed that glucose is not sufficient to provide energy during intense activity synapses, and lactate can be an effective source of energy that supports and strengthens metabolism brain.
Finally, the studyLactate-mediated glia-neuronal signalling in the mammalian brain. 2014 proved that the lactate increases the amount of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter, which is necessary for blood supply to the brain and concentration.
Lactate protects the brain from excitotoxicity, a source of energy and improves concentration.
Lactate promotes muscle growth
Lactate creates good conditions for the growth of muscles. StudyMixed lactate and caffeine compound increases satellite cell activity and anabolic signals for muscle hypertrophy. 2015 proved that the addition of caffeine and lactate increases muscle growth even during training low intensity of activating stem cells and anabolic signals: increasing the expression of myogenin and follistatin.
20 years ago, scientists discoveredLactate and the effects of exercise on testosterone secretion: evidence for the involvement of a cAMP-mediated mechanism.That after the introduction of lactate and exercise (swimming) in male mice, increases the amount of testosterone in the blood plasma. In addition, increased amount of the luteinizing hormone, which also promotes secretion testosterone. And this, in turn, has a positive effect on muscle growth.
Lactate increases the secretion of hormones necessary for muscle growth.
How to increase the amount of lactate
- Eat one hour before exercise anything rich in carbohydrates: sweet fruits, chocolate, cereals. Remember that lactate is produced when glucose decay.
- Try to give everything to the fullest. For example, try to sprint or high intensity interval training (HIIT). Arrange such training two times a week in addition to their regular loads, and gradually accustom your body to produce more lactate to increase endurance, muscle growth and brain protection.