How many calories we burn during exercise actually
Sport And Fitness / / December 19, 2019
Number of contact calories burned during physical activity depends on many factors, so that the performance on a treadmill - this is something like the average temperature in the hospital. Today we will deal with the fact what factors, in addition to weight, height, sex and age, affect the number of calories burned by us as speed up the process, as well as a look at the table with the average value of calories burned during functional training, yoga or lifting weights.
Computer in a treadmill, elliptical trainer or stepper requires only enter your age, height and weight, and then gives you the averages of the data. In order to understand how many calories you burn really need much more information.
The simulator is not able to measure the temperature of your body, and does not take into account the surrounding climate conditions, ie air temperature, humidity and the presence or absence of precipitation.
The number of calories burned affects your muscle mass, body fat percentage in the body, the level of physical fitness, metabolic rate, body temperature, ambient temperature, relative humidity, presence or absence of precipitation, atmospheric pressure, altitude, during the run - your "sail" and the direction of the wind, sleep and even your diet.
For example, T - temperature, - humidity. The combination of high Tg and high V - very heavy; High and low T B - was easier; The high and low T - normal conditions; low and high T B - very cold; low and low T B - heat transfer medium above.
Breath
With increasing physical activity increases heart rate, breathing becomes discontinuous and frequent. This is because the heart tries to pump as much oxygen for the production of muscle ATP (adenosine triphosphate). That it is the fuel for our body during exercise.
Adenosine triphosphate (abbr. ATP, Eng. APR) - nucleoside, plays a crucial role in the exchange of energy and substances in organisms; first compound is known as a universal energy source for all biochemical processes in living systems.
ATP was discovered in 1929 by a group of scientists at Harvard Medical School - Carl Lohman, Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow, and Lipman, 1941, Fritz found that ATP is a major energy carrier in cell.
The main role of ATP in the body associated with providing energy numerous biochemical reactions. As the carrier two high energy bonds of ATP is a direct source of energy for a plurality of energy consuming biochemical and physiological processes. All this synthesis reaction complex substances in the body: the implementation of the active transport of molecules across biological membranes, including the establishment of the transmembrane electric potential; of muscle contraction.
It turns out that during these intense workouts for each liter of oxygen that you breathe, burns 5 calories. Thus, if we compare two people with roughly the same physical parameters, which perform the same exercise, the more calories will burn those who breathe more often.
It also means that the less you are prepared, the harder it will be for you to exercise and the more frequent will be the heart rate and breathing. This means that the calories you will burn more than a trained person. Do you want to burn more calories - breathe more often!
tables
For running and cycling sports have special applications that together with additional gadgets (heart rate monitor and sports watch) more or less accurately find the amount spent on training calories. For example, in such models hours Garmin, both Fenix 3 and Forerunner 920XT, theoretically considered ambient temperature, and allows for application Strava bicycle weight.
But for other activities - yoga, Pilates, step aerobics, functional training, weight lifting and so on - to get at least the average data is much more difficult. For this is a special table that will give you only a general idea of the number of calories burned. But it's better than nothing. We offer you the data for the main types of training.
- Aerobic - 5.2 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Quick Dances - 7.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Football - 4.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Volleyball - 4.8 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Jumping rope - 5.6 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Classes on elliptical trainer - 7.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Climbing stairs / step - 7.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Stretching - 1.8 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Training with weights - 3.8 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Astanga yoga - 6 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Static yoga - 3.2 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- exercise cycle - 4.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Step aerobics light - 7.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Step aerobics intense - 10.6 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Velosimulator (medium load) - 7.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Velosimulator (intensive load) - 11.1 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Rowing trainer - 7.4 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
- Intensive lifting weights - 6 kcal per hour per 1 kg of weight.
Calculator to calculate the calories burned during strength training.
Since swimming is another story, because the clock does not take into account the number of calories the body spends on heating, because the water temperature is always lower than the body temperature.
Usually swimmers spend four times more energy than the athletes. Traveling at a speed of 400 m / h burns 3 kcal per 1 kg of your weight per hour, slow swimming breaststroke - 6 kcal, slow swimming crawl - 7 kcal fast swimming crawl - 8 kcal.
You can calculate the approximate number of calories burned during your workout for swimming manually and compared with the figures, which will give you an application on the basis of the data from your hours.
What is the Cooper test
If you're wondering what methods used by athletes, suggest that you try to calculate your level of fitness with the help of the Cooper test.
Cooper test - the general name of a series of tests on the physical fitness of the human body, created by the American doctor Kenneth Cooper in 1968 for the US Army. Most known kind, consisting in a 12 minute run: fixed distance, and based on these data conclusions in sports or medical purposes. Kenneth Cooper has created more than 30 such tests, however, it is this is widely used in professional sports, such as football. When the test is activated 2/3 muscle. Given that run on 5000 m world record belongs Kenenisa Bekele and is 12: 37.35, then the run is 12 minutes, he would overcome about 4800 m.
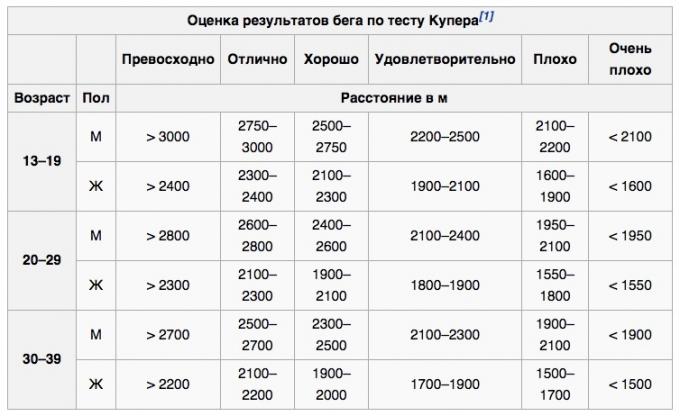
Running can be replaced by a bike or swimming for 12 minutes.



